Smart Driving System
Embedded Systems Course Final Project | Fall 2023
Overview
Collaborator | Shou-Ren Chen
This Embedded Systems final project explores how real-time sensing, wireless communication, and local computation can be integrated into a compact smart-driving assistant. Our goal was to design a system capable of reading environmental distances, detecting danger, adjusting driving modes, and supporting early-stage autonomous parking through machine learning.
Built using an STM32 board, Raspberry Pi 3, PiRacer Pro, and ToF sensors, the system demonstrates multiple embedded concepts—including BLE, PWM motor control, I²C peripherals, multi-threading, HTTP streaming, and ML-based behavioral cloning.
This Embedded Systems final project explores how real-time sensing, wireless communication, and local computation can be integrated into a compact smart-driving assistant. Our goal was to design a system capable of reading environmental distances, detecting danger, adjusting driving modes, and supporting early-stage autonomous parking through machine learning.
Built using an STM32 board, Raspberry Pi 3, PiRacer Pro, and ToF sensors, the system demonstrates multiple embedded concepts—including BLE, PWM motor control, I²C peripherals, multi-threading, HTTP streaming, and ML-based behavioral cloning.

Real time display of our system.
Introduction
This project integrates sensing, communication, control, and machine learning into a compact embedded system. We successfully implemented:
- Real-time distance detection
- Driving mode switching
- Danger detection and braking
- FPV video streaming
- Prototype-level auto parking
Design — System Features & Hardware
Key Features
- Real-Time Distance Measurement — Using VL53L0X ToF sensor on STM32 to continuously stream distance data via BLE.
- Driving Modes — Normal Mode (50%) and Parking Mode (22%) for fine motor control.
- Danger Detection — Automatic braking and warning messages when objects are too close.
- Live FPV Display — Raspberry Pi camera streaming video via MJPEG over HTTP, with mode and distance overlays.
- Auto Parking (Prototype) — Behavioral cloning model trained on steering + throttle pairs to imitate human parking behavior.
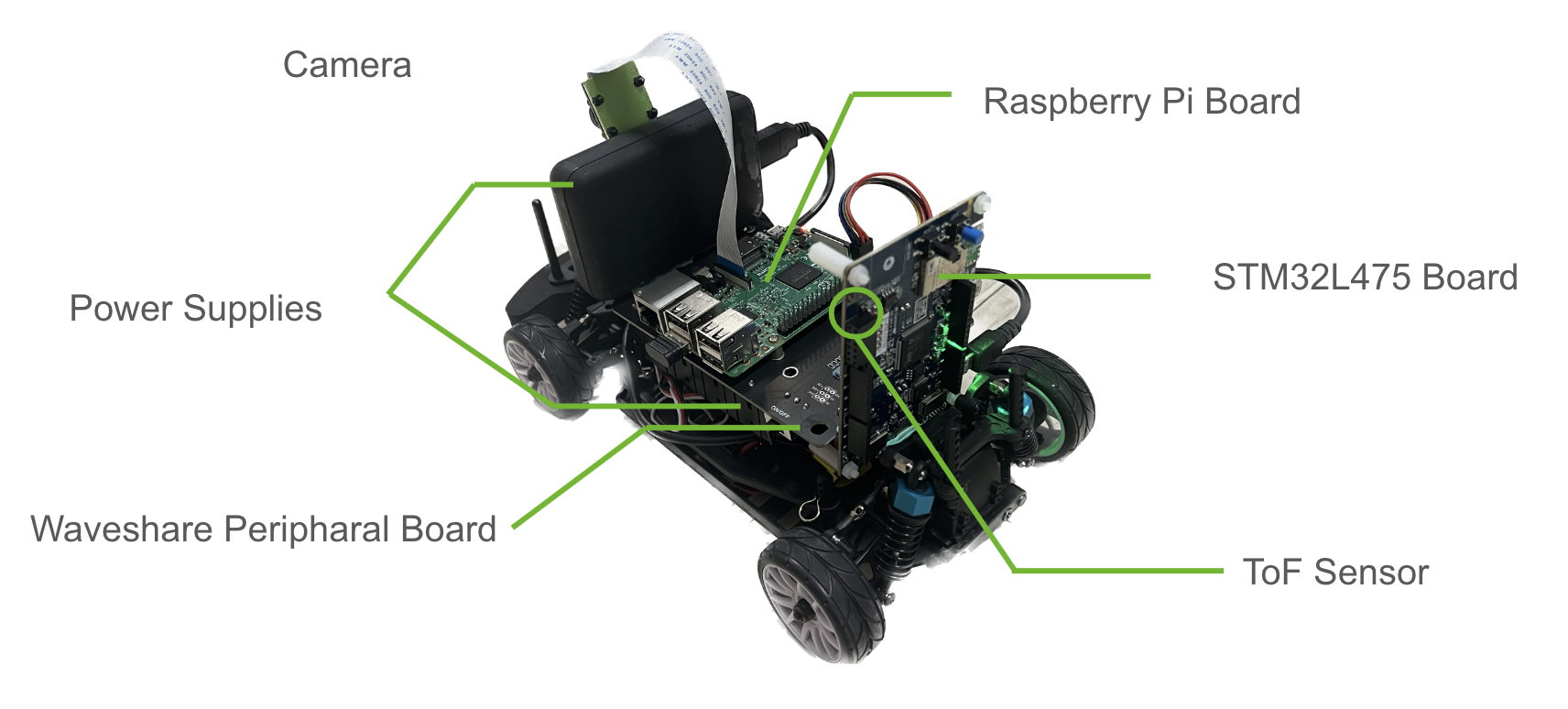
Hardware setup including STM32, Raspberry Pi 3, PiRacer Pro, ToF sensor, and wide-angle camera.
Hardware Used
- STM32L475 + VL53L0X Time-of-Flight Sensor
- Raspberry Pi 3
- PiRacer Pro platform + joystick controller
- Wide-angle FPV camera
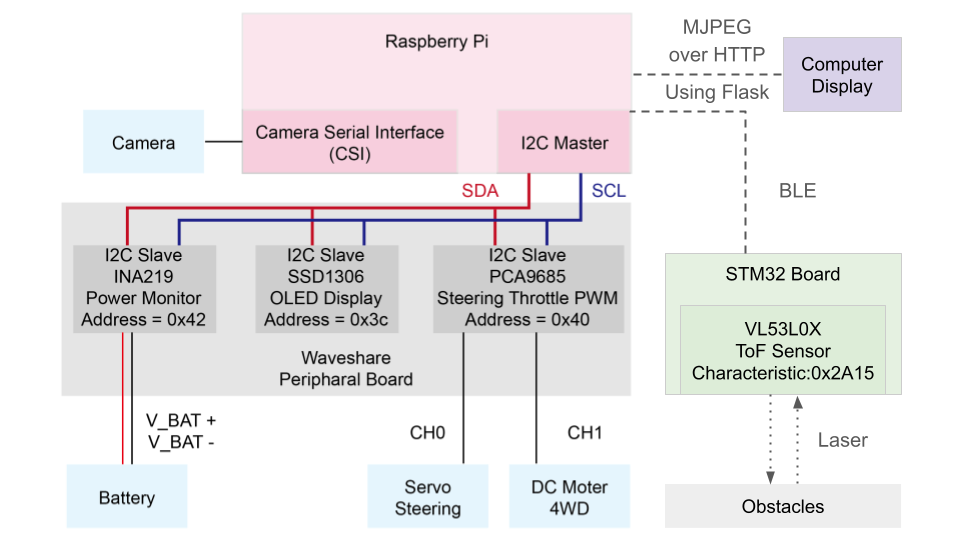
Overall architecture of communication and control modules.
Core Functionalities
Real-Time Distance Measurement
Using the VL53L0X Time-of-Flight sensor on the STM32, the system measures distance in real time in continuous polling mode. The STM32 updates the value every 300 ms and sends the distance to the Raspberry Pi via BLE.
Danger Detection
- ≥ 400 mm → Safe
- 100–400 mm → Show distance on screen as a proximity warning
- ≤ 100 mm → Trigger emergency stop and block forward movement
Driving Mode Switching
Using the joystick’s B button, the driver can switch between Normal Mode (50% speed) and Parking Mode (22% speed) for finer control in narrow spaces.
FPV Interface
- Raspberry Pi camera stream served via Flask using MJPEG
- Overlays show current driving mode and latest distance reading
Auto Parking Prototype
- Implemented using the DonkeyCar behavioral cloning framework
- CNN predicts steering and throttle from front camera images
- Trained on 10k–31k frames; achieves initial movement but fails on complex turns
More details at our github repository.